Feline Heartworm Infection: Serious
As springtime arrives throughout the U.S., the steamy days and nights of summer cannot be far behind. This means, of course, a proliferation of mosquitoes. For you, this is an annoyance. For your cat, these bothersome little creatures can pose a major health problem. Among all of the various disorders that can endanger a cats physical well-being and perhaps threaten its life, few are more insidious than feline heartworm disease, a potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when a parasitic worm called Dirofilaria immitis gets into an animals system. And the only way in which this worm can enter your cats body is through a mosquito bite.
The Truth About Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is a fairly common zoonosis (a disease that can be shared between humans and animals); 30 to 40 percent of adult humans, and roughly the same percentage of cats, have antibodies that indicate prior exposure to the organism that causes the disease. Prevention is Best. Nevertheless, its particulars are still unfamiliar to many people. The disease poses a threat primarily to fetuses and to immunosuppressed patients, but an understanding of the organisms life cycle, how transmission occurs and can be avoided, and the signs of infection can greatly reduce the risk of serious disease.
Short Takes: March 2010
Primary septic peritonitis is an abdominal infection without a primary focus, such as a perforated bowel. The most common cause in cats is feline infectious peritonitis (FIP). Unfortunately, little is known about primary bacterial septic peritonitis in cats. The investigators (" Primary bacterial septic peritonitis in cats" in the Journal of the American Animal Hospital Association, Nov-Dec 2009) examined the medical records of twelve cats diagnosed with primary bacterial septic peritonitis and identified significant characteristics associated with this condition.
Squamous Cell Cancer: Dangerous
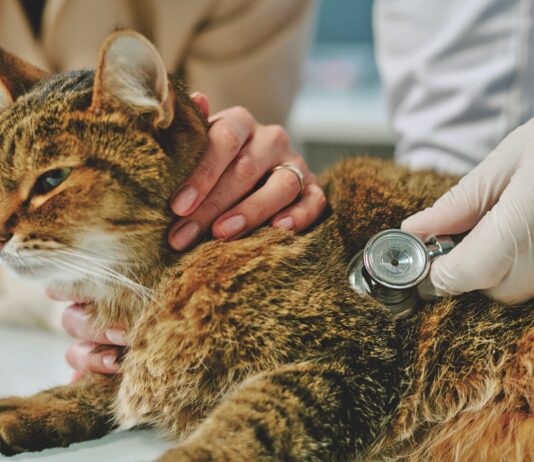
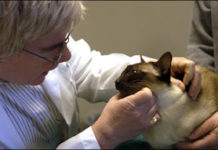
During your cats routine physical exam, youre likely to observe the veterinarian carefully studying the animals face, gently stroking its nose, and fondling its ears. This is not merely a show of affection. Rather, the veterinarian may be searching for tiny, scabby sores on the cats skin that could indicate the presence of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) - a skin cancer that, if caught in its early stage, will most likely be harmless and easily treated. If the skin eruptions go unnoticed, however, the cancer can progress, spread to other parts of the body and ultimately prove fatal.
Ask Elizabeth: March 2010
Sometimes, I find things which appear to be grains of rice stuck to the fur around my cats hind end. Figaro does go outside, but I cant figure out how he could get rice stuck back there. Do you think hes been rooting around in garbage cans looking for food?
Diagnosis: Feline Lymphoma
The feline lymphatic system an exquisitely structured arrangement of internal organs and tissues directly or indirectly influences every aspect of a cats physical existence. For this reason, owners should be equipped to recognize the signs that suggest the presence of feline lymphoma, a potentially deadly cancer of the lymphatic system that can assault many areas of a cats body, including its liver, gastrointestinal system, spleen and skin.
Herpesvirus: A Big Threat to Pets
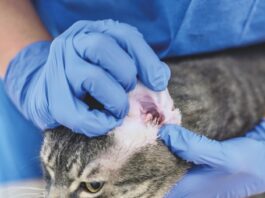
Many cats, at some point in their lives, will contract an upper respiratory disease characterized by persistent sneezing, nasal discharge, conjunctivitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane lining the inner surface of the eyelid), and in some cases keratitis (inflammation of the transparent outer covering of the front of the eyeball). Although a wide range of viral and bacterial agents may be responsible for this disorder, one of the most common - perhaps the most common - cause is infection with feline herpesvirus (FHV).
Ask Elizabeth: 12/09
Rabies is in the family of RNA viruses (Rhabdoviridae) and the genus, Lyssavirus. Rabies exists nearly everywhere although some areas (including New Zealand; parts of the Caribbean, Scandinavia, and British Isles; Japan; and Hawaii) are thought to be free of the virus.
The Real Danger of Hypothermia
Cats whose breed developed in frigid areas of the world are likely to tolerate cold weather better than cats whose origins can be traced to more temperate regions. But even the fattest, furriest Maine coon will have only a slight edge over a trim, thin-coated Siamese when it comes to prolonged exposure to the biting winds, ice, snow and sleet that come with winter. Indeed, any cat that is left outside for extended periods of time when the temperature is below freezing - not to mention any poor creature that happens to tumble into an ice-cold pond - will be at risk for a potentially deadly drop in body temperature. The chances that this condition - called hypothermia - will prove fatal depends largely upon the animals age, overall physical condition and ability to regulate its body temperature, says Dr. Gretchen Schoeffler, chief of emergency and critical care services at the Cornell University Hospital for Animals.
Short Takes: January 2010
A common disease in cats, upper respiratory tract disease (URTD) can spread quickly among cats residing in animal shelters. These infections cause discomfort in the animals, consume vital personnel and financial resources and limit adoptions. In a large urban shelter in the northeast United States, 531 kittens, 701 litters and 2,203 adult cats were observed during their stays on a daily basis over a period of 50 weeks for signs of URTD ("Descriptive epidemiology of feline upper respiratory tract disease in an animal shelter" in the Journal of Feline Medicine and Surgery, 2009).
FeLV and FIV Testing: Important
Among all causes of lethal feline disease, none should be taken more seriously by cat owners than those caused by two specific submicroscopic organisms: feline leukemia virus (FeLV) and feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV). Although these viruses are somewhat different in appearance and in the manner in which they exact their toll on feline health, infection with either one of them, if undetected, is capable of causing a cats premature death. All Too Common. To make matters worse, FeLV and FIV infections are by no means rare. Recent estimates indicate that two percent to four percent of the 83 million or so cats in the U.S. harbor one or both of these two viruses.
Diagnosis: Feline Anemia
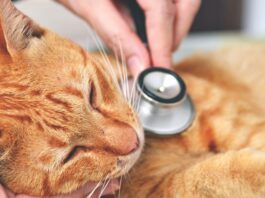
Veterinarians generally recommend that all cats undergo a thorough physical examination at least once a year until they have reached seven or eight years of age, and twice annually thereafter as they progress into their senior years. The exam should include a complete blood count (CBC), a procedure that can reveal or at least suggest the presence of many feline health disorders. The importance of the CBC should not be underestimated. Among other things, a CBC will determine the concentration of red blood cells (erythrocytes) in a drop or two of blood. The procedure will also reveal the density of hemoglobin, an important constituent of each erythrocyte.